In the fascinating world of chemistry, understanding the structure and composition of materials plays a vital role. This understanding helps us create new materials, diagnose diseases, control the quality of food products, and discover the secrets of nature. One of the most powerful tools available for analyzing chemical compounds is Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS).
Introducing Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS): A Key to Understanding the World of Molecules
Chemical analysis is a process by which the nature, composition, and structure of materials are examined. This process is used in all branches of science and industry. From discovering new drugs and developing advanced materials to controlling the quality of food and monitoring environmental pollution, all rely on accurate and efficient methods for chemical analysis.
There are various methods for chemical analysis, each with its own specific features and applications. Some common methods include:
- Spectroscopy: In this method, light or electromagnetic waves interact with the material, and information about the molecular structure of the material is obtained from the absorption or emission pattern of these waves.
- Chromatography: In this method, a mixture of different compounds is passed over a column. Each compound leaves the column at a different rate, and thus the components of the mixture are separated from each other.

Main Steps of the LC-MS Process
LC-MS consists of three main steps:
- Separation: In this step, a mixture of different compounds is separated from each other using liquid chromatography. Each compound, according to its physical and chemical properties, passes through the chromatography column at a different rate.
- Ionization: In this step, the neutral molecules in the sample are converted into ions. There are different methods for ionization, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Mass Analysis: In this step, the mass-to-charge ratio of the ions is measured by a mass analyzer. Based on this information, the identity and structure of the molecules in the sample can be determined.
Main Components of the LC-MS Device
The LC-MS device consists of various components, each of which has a specific function:
- Liquid Chromatography System: This system includes a pump, column, and other components and is responsible for separating the compounds in the sample.
- Ionization Source: This section is responsible for converting neutral molecules into ions. There are different methods for ionization, the most common of which include electrospray ionization (ESI) and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI).
- Mass Analyzer: This section is responsible for measuring the mass-to-charge ratio of the ions. There are different types of mass analyzers, the most common of which include quadrupole mass spectrometer, TOF mass spectrometer, and magnetic-field mass spectrometer.
Ionization Mechanism in LC-MS
In the LC-MS ionization process, the neutral molecules in the sample are converted into ions. This is done by various methods, including electrospray ionization (ESI) and atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI).
In electrospray ionization, the sample is dissolved as a solution in a liquid solvent and injected into the ionization source. Then, by applying a high voltage to the solution, fine droplets are created from it. These droplets lose their charge due to solvent evaporation and turn into ions.
In atmospheric pressure chemical ionization, the sample is injected as a gas into the ionization source. Then, by applying a high voltage to the gas, the molecules are ionized.
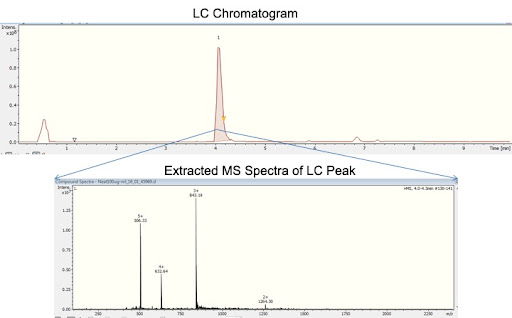
Interpretation of Results from LC-MS
The results from LC-MS are presented as mass spectra. A mass spectrum is a diagram in which the mass-to-charge ratio of the ions is plotted on the x-axis and the signal intensity is plotted on the y-axis.
By interpreting the mass spectrum, various information such as the identity, structure, and concentration of the compounds in the sample can be obtained.
Applications of LC-MS
Due to its high sensitivity, excellent resolution, and ability to identify and quantify several compounds simultaneously, LC-MS has very wide applications in various fields.
Here are some of the most important applications of LC-MS:
Food Analysis:
- Identifying and quantifying nutrients, vitamins, additives, and contaminants in food
- Controlling the quality of food and ensuring its safety
- Studying the taste and aroma of food
- Developing new food products
Pharmaceutical Analysis:
- Identifying and purifying drugs
- Studying the metabolism of drugs in the body
- Developing new drugs
- Controlling the quality of drugs
Environmental Analysis:
- Identifying and quantifying pollutants in water, soil, and air
- Monitoring environmental quality
- Studying the effects of pollutants on the environment
Applications of LC-MS in Scientific Research:
- Proteomics: Studying proteins and their role in cells
- Metabolomics: Studying metabolites and their role in living organisms
- Biochemistry: Studying the structure and function of biological molecules
- Forensic medicine: Identifying criminals and solving crimes
- Materials science: Studying the properties and structure of materials
Advantages and Disadvantages of LC-MS
Advantages:
- High sensitivity: LC-MS can identify and quantify very small amounts of compounds in samples.
- Excellent resolution: LC-MS can separate compounds with very similar structures from each other.
- Ability to identify and quantify several compounds simultaneously: LC-MS can simultaneously identify and quantify several compounds in one sample.
- High speed in analysis: LC-MS can analyze samples quickly and accurately.
- Automation capability: The LC-MS process can be fully automated.
Disadvantages:
- High cost of equipment: LC-MS devices are very expensive, which can be a barrier to the use of this technique by some individuals and organizations.
- Need for experienced operator: Working with the LC-MS device requires expertise and experience.
- Complexity of the sample preparation process: The sample preparation process for LC-MS can be complex and time-consuming.
The Future of LC-MS
LC-MS is a developing technology, and significant advances are being made in this field. In the coming years, we will see increased sensitivity, speed, and accuracy of LC-MS. Also, new applications will be found for this technique in various fields, including medicine, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and environmental science.
Conclusion
LC-MS is a powerful tool for analyzing chemical compounds with very wide applications in various fields. Considering the numerous advantages of this technique, it can be expected that in the coming years we will see increasing use of LC-MS in various industries.